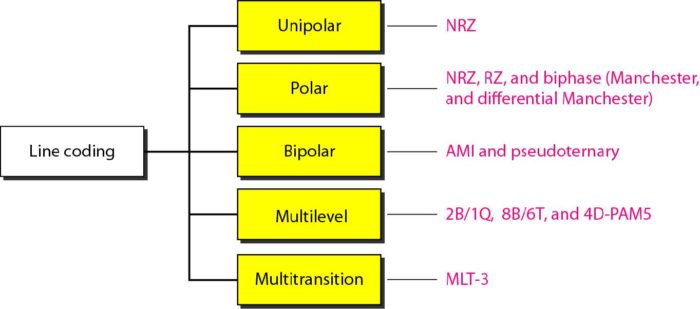
Line Coding
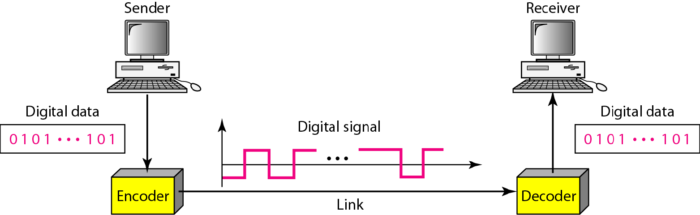
Introduction
The process of converting digital data to digital signals. Digital data – sequences of bits.
Characteristics
- Data rate vs. signal rate
- Data rate (bit rate) – the number of data elements in a unit time (bps).
- Signal rate (pulse, modulation rate, baud rate) – the number of signal element in a unit time (baud).
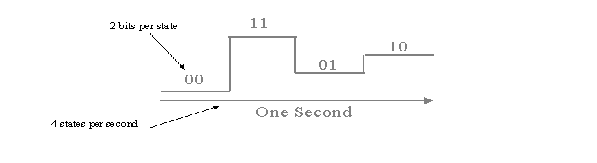
- No. of Signal Levels
- Two data levels,
Two Signal levels
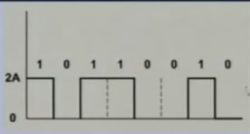
- Two data levels
Three signal levels
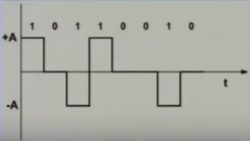
- Two data levels,
- DC components
- It is the mean value of the waveform. If the mean amplitude is zero, there is no DC offset.
- unable to pass a low-pass filter or Over one cycle period if all positive voltage are cancelled by negative volatge then the DC component of the waveform is zero.
- In line coding, the signal with non-zero dc component is treated as distorted one and it can create errors in the received signal.
- Bandwidth
- Although the actual bandwidth of a digital signal is infinite, the effective bandwidth is finite.
- Self synchronization
- the clocks at the sender and the receiver must have the same bit interval. If the receiver clock is faster or slower it will misinterpret the incoming bit stream.