Grand Unified Boot loader (GRUB)
GRUB
- GRUB is an operating system independent boot loader
- A multiboot software packet
- Flexible command line interface
- File system access
- Support multiple executable format
- Support diskless system
- Download OS from network
- GNU GRUB is a Multiboot boot loader.
- It was derived from GRUB, the GRand Unified Bootloader, which was originally designed and implemented by Erich Stefan Boleyn.
- Briefly, a boot loader is the first software program that runs when a computer starts.
- It is responsible for loading and transferring control to the operating system kernel software
- The kernel, in turn, initializes the rest of the operating system
GRUB boot process
- The BIOS finds a bootable device (hard disk) and transfers control to the master boot record
- The MBR contains GRUB stage 1. Given the small size of the MBR, Stage 1 just load the next stage of GRUB
- GRUB Stage 1.5 is located in the first 30 kilobytes of hard disk immediately following the MBR. Stage 1.5 loads Stage 2.
- GRUB Stage 2 receives control, and displays to the user the GRUB boot menu (where the user can manually specify the boot parameters).
- GRUB loads the user-selected (or default) kernel into memory and passes control on to the kernel.
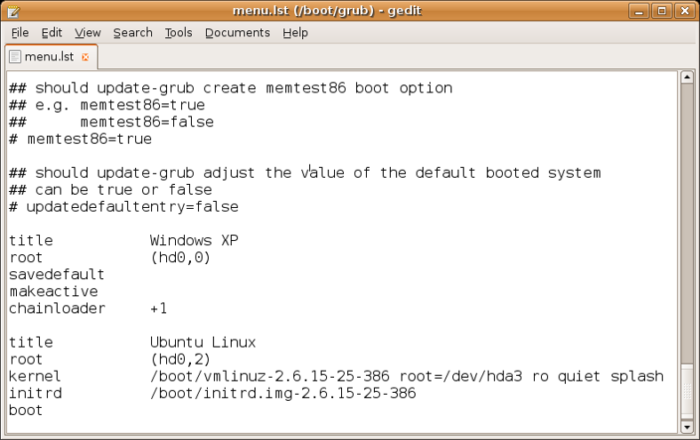
GRUB Config File
GRUB 2
- Derived from PUPA (Published Unexamined Patent Application) research project, Japan
- Next generation of GRUB
- Rewritten from scratch to clean up everything for modularity & portability
- Goals:
- Scripting support
- Graphical Interface
- Dynamic loading of modules
- Portability for various architecture
- Internationalization
- Real memory management
- Object-oriented framework for file system
- Cross platform installation
- Fix design mistakes in GRUB legacy