Free Space Management
- Since disk is limited, we need to reuse it
- To keep track of free disk space, system maintains a free space list
- Free space list records all free disk blocks
- New file allocation is done amongst the free disk block
- When file is deleted, its disk space is added to free space list
Bit vector – approach 1
- Frequently, free space list is maintained as a bit map or bit vector
- Each block is represented as 1 bit
- If block is free, bit is 1
- If block is allocated, bit is 0
- For eg. consider disk where blocks 2,3,5,7,8,10 are free and rest are allocated. The free space bit map would be 0110 1011 01
- Advantage – relatively simple and efficient to find first free block
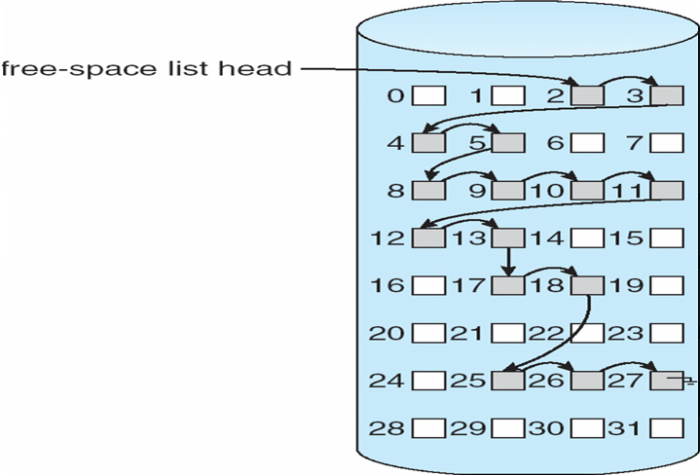
Linked list – approach 2
- Free blocks are linked with each other
- First block contains pointer to next free block and so on
- Scheme is not efficient as list traversing needs substantial I/O time
Grouping- approach 3
- Store address of n free block in the first free block
- The first n-1 of these blocks are actually free
- The last block contains addresses of another n free blocks
- Address of large number of free blocks can now be found quickly
Counting- approach 4
- Generally several contiguous blocks are allocated or freed simultaneously
- So idea is to keep address of first block and number n of free contiguous blocks that follow first block
- Now each entry in free space list then consists of disk address and a count
Disk management
- A storage device mechanism by which the computer may store some information in such a way that this information may be retrieved at a later time
- Size of main memory is small to accommodate all data and programs and loses data when power is lost
- Operating system is responsible for:
- free space management
- storage allocation
- disk scheduling
- In UNIX / Linux, every thing is consider as file
- For eg. if you have two hard disks then representation will be
- /dev/hda (primary master HDD)
- /dev/hdb, (primary slave HDD)
- For floppy drive – /dev/fd0
- For CD ROM – /dev/cdrom
- For DVD-writer – /dev/dvdwriter
- USB mass storage – /dev/sda
Swapping
- Swap space management is a low level task of operating system
- The main goal for the design and implementation of swap space is to provide best throughput for the virtual memory system
- Swap device is a block device in configurable section of a disk
- Kernel allocates contiguous space on the swap device without fragmentation
- Free space of swap device is maintained in core table – map
- Kernel treats each unit of swap map as group of disk blocks
- As kernel allocates and frees resources, it updates map accordingly
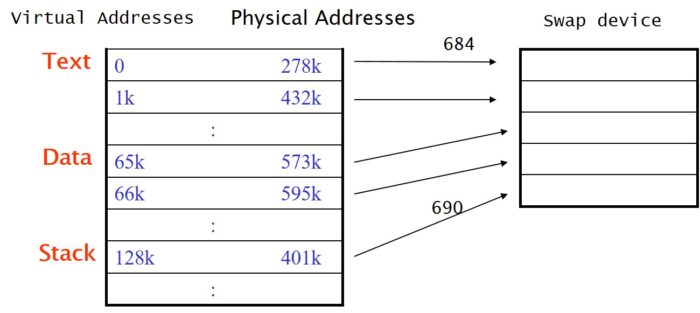
Mapping process to swap device. Here, Swap out.